Know Your Generator- Quick Guide on Everything you need to Know
Types and Categorization:
Generators differ by size, application and type of mechanical energy employed to generator power.They are often categorized by their external source, or mechanical energy. To talk about various generators therefore involves types of electric power generation. In other words, what they run on.
Petrol / Gasoline
Typically used for short periods and mostly for portable generators. They may be expensive run because of the prices of petrol / gasoline
Diesel
Most popular fuel for industrial generators
Natural gas
Generators rely on underground access to natural gas; more environmentally friendly than gasoline or diesel. These type of generators are not common in Africa and especially in our country Kenya
Propane
Another greener alternative to diesel and gasoline; often the choice for fuel when natural gas isn’t an option. These type of generators are not common in Africa and especially in our country Kenya



Other External Sources
Include wind, solar, hydro (water), coal and nuclear energy, which are mostly used by generators in power plants to harness power for the grid and hydrogen, typically used in laboratories. Homes, businesses, medical centres and hospitals tend to rely on diesel, gasoline or natural gas to convert to electricity.
Types of generators by Application
Typical generator examples by application: portable, inverter, standby and industrial.
Portable generators
Portable units typically power essential small appliances in the home, in small businesses or events where direct electricity is not available. As the name implies, these are movable generators. If powered by gasoline, they typically run anywhere between 7.5 hours to 12 hours. We said “typically,” because a few can operate for 18 or even 24 hours. That said, the running time depends on load, which refers to how much power is being generated and what the generator is powering. The fuel tank is located inside the generator and appliances or devices and be plugged directly into the generator’s sockets.
Portable industrial generators, which can also do the job of commercial portable generators, are also available, and can run for less than 16 hours, powering multiple appliances. These can vary in size. Some are too large to be carried but can be placed on a trailer and taken to, for example, a construction site.
Portable generators usually use gasoline, diesel or natural gas. Some even rely on propane, which is more energy efficient than natural gas, but heavier. Propane is mainly used for caravans as it can run for days – some can even last for just over a week. Most portable units tend to be noisy, as they lack sound insulation. More models are appearing on the market today that address this issue.
Inverter generators
They are lightweight and compact, these actually fit the portable-generator definition, yet are considered to be a category all their own. Powering electronics with a generator can be tricky, but this is where inverter generators are invaluable. While they have many applications, they’re particularly useful for computers, microwaves, mobile phones and other sensitive electronic equipment that need certain values of voltage and frequencies.
Their build differ from other portable generators. In terms of currents, the power from the engine is a high-frequency AC. It’s then converted into DC by the alternator. The generator has an inverter, which converts the current back to AC.
These extra steps in generating electricity, and the fact that the initial AC is high frequency, mean the current is more stable, which leads to less harmonic distortion. Thus, the electricity is as good as that provided by the mains electrical supplier. This also translates to energy efficiency – the generator adjusts its voltage to exactly what the connected load requires, no more, no less.
Popular as a type of generator for home, these units are also available as industrial inverter generators for use on construction sites and other demanding environments.
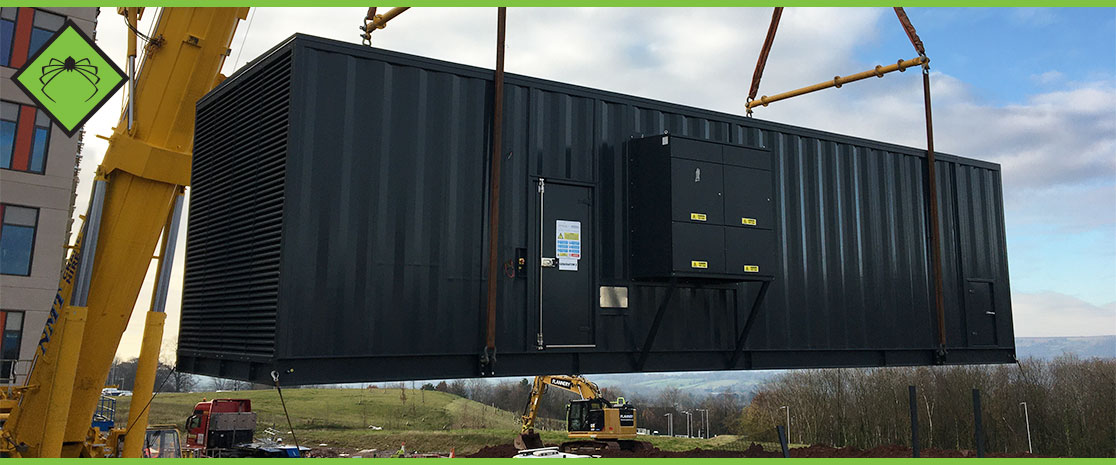
Heavy Duty Standby Generators
The standby-generator definition usually refers to heavy duty power backup fixed to the ground or on tow systems. They may also have special enclosures made, but not always. They are obviously larger than portable units and are available for both residential and industrial applications.
Standby generator types are usually powered by natural gas, diesel, or propane. Diesel powered types are more common in Africa and especially our country Kenya. When a power outage occurs, the automatic transfer switch (ATS) disconnects from the main power supply and transfers the electrical load to the generator. When power is restored to the mains, the ATS switches you back over.
The running time of a diesel-engine generator is limited by the size of the tank. As standby generators can be large, they’ll also have larger tanks. Standby generators that operate on diesel can run for 24, 48, 72 hours – and some, even longer. Open-set, or uncovered, diesel generators create noise at high decibels. Placing either generator in an enclosure designed to reduce noise can help.
Generators with Canopy
This is a generator cover, and if sound-proofed, can help with noise. It also provides protection against the elements. Placing a canopied generator within an enclosure can add an important level of security and additional protection against weather.
Industrial generators
These are typically standby generators, but on a different scale. They operate in an industrial environment where power is in high demand for everything from robotics, machinery and lighting systems to computing centres. For this reason, these units are large-capacity generators, robust and able to supply a long, continuous supply of electricity. Consequently, they need to be large and powerful.
Industrial vs. commercial generators
These are often be used synonymously, but they are different. You know an industrial-size generator when you see it. Most of today’s industrial generators are designed to supress noise with components such as heavy-duty vibration mounts, which absorb shock and vibration. An industrial generator can be found in power plants and some hospitals. Commercial generators are typically not as large, nor do their applications and environment demand the same level of power. Medical centres, residential and office blocks would typically make use of these generators, depending on their needs.
Types of diesel engines
The two types of diesel engines are two-stroke and four-stroke. Typical diesel engines rely on the four-stroke cycle, while larger engines use the two-stroke cycle.
There are four stages of the engine’s operation: intake, compression, ignition and exhaust. In the two-stroke cycle, these four stages occur in one 360˚ revolution of the crankshaft. In a four-stroke engine, the stages take two complete revolutions.
Advantages of diesel generators
Value – diesel generators tend to be more cost effective than other generator types, with a lower purchase price
Fuel efficiency – diesel has a higher thermal efficiency than gasoline generators, which makes it cheaper to operate
Durability – tough engines that stand up to different environments and conditions
Low maintenance – fewer parts need replacing and even then, the cost of parts is less than gasoline generators
Longevity – as long as the generator is maintained properly, users can expect years of use
Disadvantages of diesel generators
High CO2 emissions –technologies have made strides in lessening diesel generators’ carbon footprint, but still have a long way to go
Noise – Noise pollution can be high if measures aren’t taken to dampen the sound
Weight – diesel generators are heavy and not easily moved
Corrosion – must be kept in a dry place to prevent corrosion